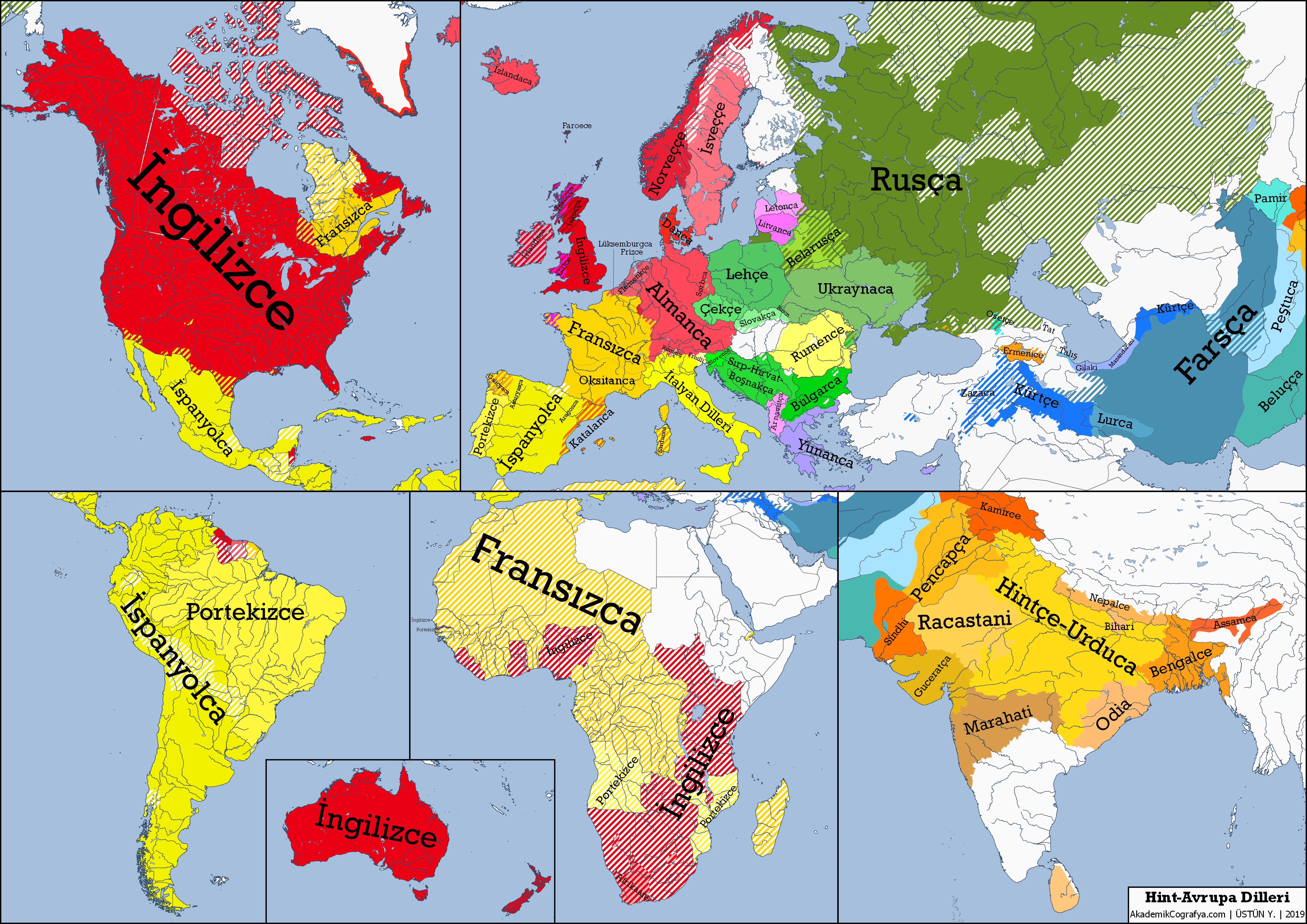
Indo-European languages form a vast family encompassing over 400 distinct languages spoken by more than 40% of the global population today. Recent landmark studies have unveiled their intriguing origin, tracing it back to the Caucasus Lower Volga region in Russia around 6,500 years ago. This revelation was made possible through groundbreaking genetic evidence, linking these ancient speakers to the Yamnaya people, who are often credited as the carriers of the proto-Indo-European language. These nomadic pastoralists not only spread their language but also exchanged cultural practices that would shape various civilizations across Europe and Asia. Understanding the origin of Indo-European languages not only enhances our knowledge of linguistic evolution but also provides insights into the migration patterns and genetic connections of ancient human populations.
The study of Indo-European languages, commonly associated with a multitude of tongues across Europe and Asia, traces its roots to a fascinating historical narrative. Known colloquially as the family of languages that includes notable examples like Latin, Greek, and Hindi, these languages emerged as speakers migrated and interacted over millennia. Research has recently spotlighted a significant cultural group believed to be the initial benchwarmers of this linguistic tradition, known as the Caucasus Lower Volga people. This group, linked to the renowned Yamnaya civilization, has contributed immensely to the understanding of language’s evolution and the genetic tapestry of populations today. By examining both archaeological findings and DNA analyses, scholars are gradually piecing together the complex story behind the dispersal of these ancient languages.
Understanding the Origins of Indo-European Languages
The Indo-European languages represent a vast family of tongues that includes many of the world’s dominant languages, such as English, Spanish, and Hindi. Their origins have fascinated linguists and historians alike. Recent studies indicate that the Indo-European languages trace back to the Caucasus Lower Volga region in Russia, around 6,500 years ago. This timeline corresponds to the Eneolithic period when early agrarian methods began to emerge, making it a significant era in human cultural development and linguistic evolution.
Research conducted at Harvard University utilized advanced DNA sampling techniques to uncover genetic connections among ancient populations, including the Yamnaya people, who played a crucial role in developing these languages. The studies revealed that these populations intermixed, leading to the spread of proto-Indo-European languages across vast distances, from Western Europe to the Indian subcontinent. Understanding these origins provides insights into how language, culture, and migration patterns have shaped contemporary societies.
The Role of the Yamnaya People in Language Dissemination
The Yamnaya people are considered pivotal in the evolution and dissemination of Indo-European languages. As nomadic pastoralists, they mastered the use of horse-drawn wagons, enhancing their mobility and enabling them to traverse vast territories. This mobility allowed them to spread not just agricultural innovations but also their languages across Europe and into parts of Asia. Their ability to move quickly and efficiently across the steppes facilitated the contact and integration of diverse cultural groups, thereby impacting the linguistic landscape significantly.
Genetic evidence further supports the assertion that the Yamnaya were key carriers of proto-Indo-European languages. Studies show that they mixed genetically with various indigenous populations along their migratory paths. This mixture brought about cultural exchanges that ultimately led to the adoption of Indo-European languages in regions as far-reaching as Mongolia and Ireland, illustrating the profound impact of the Yamnaya on global linguistic development.
The Genetic Evidence Behind Language Evolution
Genetic research provides compelling evidence regarding the origins of Indo-European languages, particularly through the analysis of DNA from ancient populations. Studies from Harvard’s Reich lab utilized genetic data from 354 individuals across archaeological sites in Russia and Southeastern Europe. This analysis traced the ancestral lines back to the Caucasus Lower Volga. It highlights how genetic mixing among these early populations contributed to the formation of distinct language groups within the Indo-European family.
The data revealed not only the migration patterns of the Yamnaya but also their unexpected influence on language development in Anatolia. Although previous theories postulated a direct descent of Anatolian languages from proto-Indo-European, the latest findings suggest that these languages might originate from an even deeper ancestral lineage. This newfound understanding emphasizes how genetic research can illuminate complex historical narratives surrounding language origins and migration.
Cultural Practices and Their Significance
Alongside their linguistic contributions, the Yamnaya culture carried certain traditions that have left a lasting mark in archaeology. One of these notable practices includes the construction of kurgans—large burial mounds used to inter their dead. These burial sites not only reflect the Yamnaya’s social structures but also their beliefs surrounding the afterlife, which were likely integral to their identity. The kurgans dotting the landscape of their homeland continue to intrigue archaeologists and serve as critical sites for understanding the life and practices of these early peoples.
The continuity of burial practices between the Caucasus Lower Volga people and the later Yamnaya underlines the significance of cultural legacy in human history. Such practices reveal how these early societies were tied to their ancestors, guiding them in creating a cohesive identity while navigating the complexities of an expansive and often hostile landscape. This shared culture, interlaced with their language, illustrates how traditions can endure and evolve across generations.
The Linguistic Legacy of Proto-Indo-European
The linguistic legacy of proto-Indo-European is vast and intricate, with their descendants forming one of the world’s most extensive language families today. Investigations into this ancient tongue have revealed common roots and structures that resonate across various languages spoken in Europe and parts of South Asia. This linguistic unity hints at a shared cultural heritage that has persisted despite significant geographical and temporal divides.
Scholars have traced numerous elements of syntax and vocabulary back to proto-Indo-European, bolstering the theory of a common ancestor language. Understanding the linguistic features that are preserved and transformed over millennia provides insights into how languages evolve in response to sociocultural changes. The study of these ancient languages not only enriches our appreciation of linguistic diversity but also highlights the profound connections built through shared ancestry.
Migration Patterns of the Indo-European Language Family
The expansion of Indo-European languages is closely tied to migration patterns throughout history. Starting from their origins in the Caucasus Lower Volga area, these early speakers ventured into new territories, leading to significant linguistic diversity. The movement of people across the steppes facilitated encounters with other linguistic groups, resulting in the exchange and transformation of languages as populations adapted to their new environments.
As populations migrated, they brought their languages with them, leading to the emergence of dialects and new language branches. The movements of the Yamnaya people, in particular, illustrate how cultural and linguistic shifts were often synchronized with migration, amplifying their impact. The migration-driven evolution of these languages continues to be a subject of study, reflecting how historical events shaped the linguistic landscape we know today.
The Relationship Between Genetics and Language Families
The relationship between genetic ancestry and language families is an emerging field of interest for researchers aiming to understand how our genetic makeup influences language development. Studies investigating the population genetics of the Yamnaya have unveiled significant correlations between genetic markers and the regions where Indo-European languages proliferated. These findings illustrate how genetics can serve as a guide in tracing the paths of ancient languages and their speakers.
By examining genetic lineage alongside linguistic data, scientists are uncovering a more nuanced picture of how ancient societies interacted and shared cultural knowledge. Every layer of genetic data enhances our understanding of how populations merged, separated, and ultimately contributed to the rich tapestry of languages spoken today. This interdisciplinary approach fosters a holistic understanding of linguistic evolution, highlighting an intricate relationship between genetics and language.
The Impact of War on Linguistic Research Developments
The ongoing conflict in Ukraine has highlighted the fragile nature of collaborative linguistic research, especially in light of significant discoveries related to Indo-European languages. The war has posed challenges for researchers who rely on shared knowledge and resources, evident in the publication of two separate papers emanating from the same groundbreaking studies. This fragmentation reflects not only the current geopolitical climate but also emphasizes how external conflicts can disrupt academic collaboration and the pursuit of knowledge.
Despite these challenges, researchers are determined to continue their work, leveraging the data they have gathered to piece together the historical narratives that shaped Indo-European languages. There remains a hope that, once stability returns, these collaborative efforts can continue, leading to richer insights and a more unified understanding of how the Indo-European language family developed over millennia. The resilience of the academic community in the face of adversity ensures that critical discoveries will not be lost.
Future Directions in Indo-European Language Studies
The future of Indo-European language studies promises exciting developments grounded in rapid advancements in genetic research and linguistic analysis. As new techniques emerge, researchers will be better equipped to delve into the complexities of language evolution, cultural exchange, and migration. For example, combining linguistic data with detailed genetic profiles presents an opportunity to understand the interplay between language and identity more deeply.
Moreover, as the field opens to interdisciplinary collaboration, it is likely that insights from archaeology, anthropology, and history will further enrich our understanding of Indo-European languages. As researchers continue to decode the past, important questions regarding the origins, diffusion, and transformation of languages will be addressed, fostering a comprehensive picture of how human societies communicate. The goal remains to illuminate the past while informing the future of linguistic studies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the origin of Indo-European languages and how are the Caucasus Lower Volga people connected to it?
The origin of Indo-European languages can be traced back to the Caucasus Lower Volga people, who lived around 6,500 years ago in present-day Russia. Genetic evidence suggests that these ancient populations were integral in the development of proto-Indo-European, the ancestor of the Indo-European language family, which now encompasses over 400 languages worldwide.
How do genetic findings support the theories about the Yamnaya people and the spread of Indo-European languages?
Genetic findings support theories of the Yamnaya people’s role in spreading Indo-European languages by showing their migration from the steppe regions of Russia and their mixing with other local populations in Europe and Asia. This genetic evidence aligns with historic linguistic patterns, suggesting the Yamnaya shared the proto-Indo-European language as they expanded.
What role did the Yamnaya culture play in the dissemination of Indo-European languages?
The Yamnaya culture played a critical role in the dissemination of Indo-European languages through their nomadic lifestyle and advanced pastoral practices, such as horse riding and wagon usage. As they migrated across vast distances, they carried their language, influencing local populations from the steppes of Eurasia to regions such as India and Ireland.
What is proto-Indo-European and how is it linked to the Caucasus Lower Volga people?
Proto-Indo-European is the reconstructed ancestor language of the Indo-European family. Recent studies indicate that the Caucasus Lower Volga people were likely descendants of these early proto-Indo-European speakers, marking them as a cultural and linguistic source for many modern languages.
What evidence exists for the genetic diversity among early speakers of Indo-European languages?
Research shows significant genetic diversity among early speakers of Indo-European languages, particularly from populations such as the Yamnaya and those from the Caucasus. These ancient groups exhibited mixing with local populations, contributing to the genetic and linguistic tapestry of Europe and Asia.
How does archaeology contribute to our understanding of Indo-European languages?
Archaeology provides essential context for understanding Indo-European languages by unearthing artifacts and burial practices, like kurgans. These findings help reconstruct the cultural practices of the Yamnaya and associated populations, linking physical evidence with linguistic development.
What are the implications of the recent findings on Indo-European languages for modern linguistics?
Recent findings on Indo-European languages, especially the links to the Caucasus Lower Volga people and Yamnaya culture, have significant implications for modern linguistics by adding a genetic dimension to historical language studies, enriching our understanding of language evolution and migration patterns.
Why is the study of the origins of Indo-European languages important?
Studying the origins of Indo-European languages is essential as it uncovers the historical and cultural narratives of humanity, revealing how languages spread, evolve, and influence modern societies. It helps understand the interconnectedness of various cultures through their linguistic heritage.
| Key Findings | Details |
|---|---|
| DNA evidence identifies Indo-European language origin | Origin traced back to Caucasus Lower Volga people in present-day Russia, approximately 6,500 years ago. |
| Spread of Indo-European languages | Languages spread from the steppe to regions across Europe and into the Indian subcontinent. |
| Influence of Yamnaya people | The Yamnaya people were significant in the dissemination of proto-Indo-European languages around 5,000 years ago. |
| Collaborative research efforts | Combining genetics, archaeology, and linguistics has provided a clearer picture of Indo-European languages. |
| Impact of the Russia-Ukraine war | Current geopolitical challenges have affected collaboration among researchers studying Indo-European origins. |
Summary
Indo-European languages have a rich and complex history, and recent landmark studies have pinpointed their origins in the Caucasus region of present-day Russia. This genetic research illuminates how ancient cultures, such as the Yamnaya people, played a critical role in the spread of these languages across vast distances from Europe to Asia. Understanding the development and diffusion of Indo-European languages not only adds to our knowledge of linguistic evolution but also showcases the interplay between genetics, culture, and migration throughout history.